I. XPS and XRD
1. Refrences
- Engineering Interface and Oxygen Vacancies of NixCo1–xSe2 to Boost Oxygen Catalysis for Flexible Zn–Air Batteries ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31, 27964–27972
- Unraveling the Influence of Oxygen Vacancy Concentration on Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to Formate over Indium Oxide Catalysts ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 6, 4021–4029
2. Typical Reasons for the Formation of OXygen Vacancies
The formation of VO″ may be caused by the following factors: (i) the lattice O was oxidized to O2 during polarization and (ii) Se on the surface may be oxidized to Se element and peeled off, thus leading to oxygen vacancies.[ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31, 27964–27972]
3. XPS O1s Deconvolution
Ref [ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31, 27964–27972]
- the O1 area at 530.2 eV corresponds to metal–O bond.
- The O2 at 531.8 eV corresponds to VO″.
- The O3 (532.9 eV) is associated with hydroxy species or adsorbed water molecules
Ref [ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 6, 4021–4029]
The O 1s XPS spectra of the three In2O3 samples were deconvoluted into three peaks, corresponding to lattice oxygen (In–O, ∼529.7 eV), oxygen vacancies (∼531.4 eV), and chemisorbed oxygen (∼532.5 eV), respectively.
Ref [https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.122775]
BiVO4 has lattice oxygen (OL) at 529.7 eV and an oxygen vacancy (OV) at 531.7 eV [30], [31]. The ESR results also proved that there were oxygen vacancies on BiVO4, B-Sm4 and α-Fe2O3 (Fig. S5). This is an inherent defect in the materials [14]. With the modification of the catalyst, the incorporation of metal Sm slightly decreased the OL, indicating that metal Sm interacted with O. The oxygen vacancy of B-Sm4 became 530.8 eV and that of B-Sm-F became 531.1 eV. The decrease in the OV binding energy indicates that the electrons around the OV are enriched. This may be due to the electron transfer around Bi, resulting in the loosening and fracture of the chemical bond between Bi and O and the subsequent generation of oxygen vacancies.
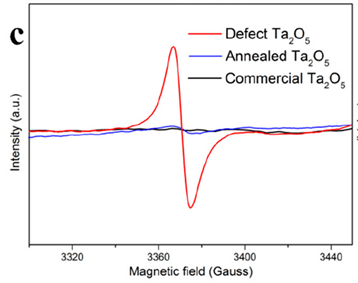
4. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) or electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy
Mechanism: the fact that a single electron can be captured or trapped by surface oxygen vacancies in catalysts.
EPR can not only probe the defects directly with high sensitivity but also determine the type of defects by a g factor value.[J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 26, 16268–16280]
Operation:
Operation
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) measurements were run on a Bruker EPR A300 spectrometer at 77 K
ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 15, 9437–9445
a
ESR spectra were measured at 300 K using an ESR spectrometer (JEOL JES-FA200) at 9.08 GHz
ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 2, 1077–1085
Low temperature electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) of solid sample was taken on Bruker-A300-10/12 spectrometer and measured at 77 K. In addition, the EPR signals of radicals were also examined on Bruker-A300-10/12 spectrometer at room temperature
ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 17, 11256–11265
no signal was detected for the In2O3 prepared in the air, while significant peaks located at g = 2.001 were observed for P-In2O3 and R-In2O3, indicating a much higher oxygen vacancy concentration in the In2O3 sample prepared in an NH3 and a H2 atmosphere
ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 6, 4021–4029


Leave a comment